Polymorphism
| Feature | Compile-time (Static) | Runtime (Dynamic) |
|---|---|---|
| Binding | Compile-time | Runtime |
| Mechanism | Overloading, Templates | Virtual functions |
| Flexibility | Limited | High |
| Speed | Faster | Slight overhead (vtable) |
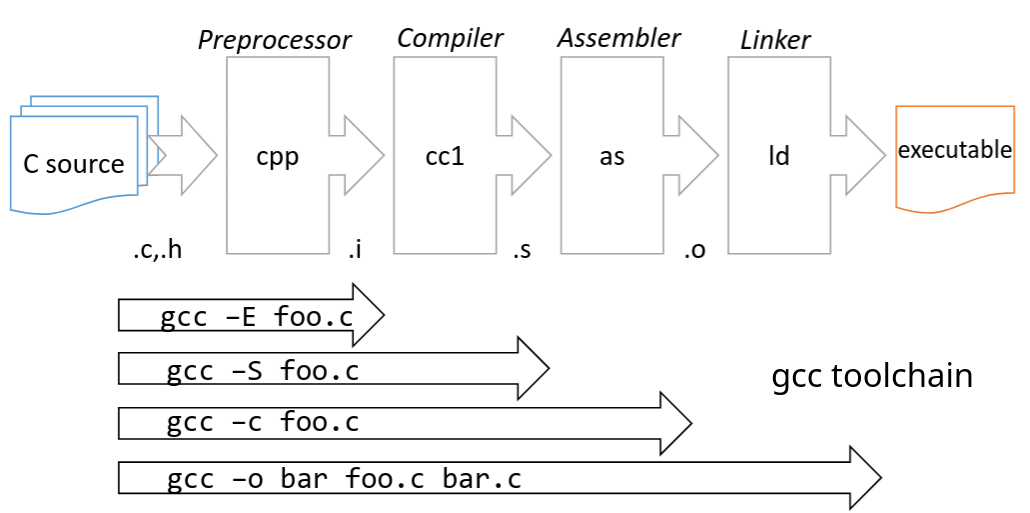
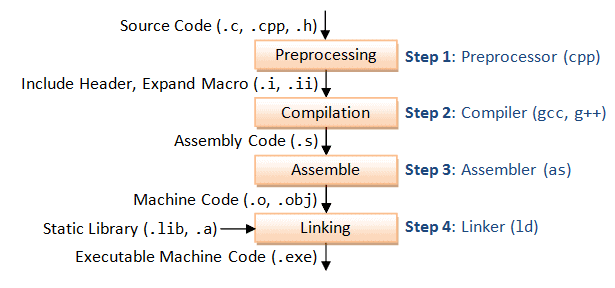
| compile-time: |
add(int, int);
add(double, double);
runtime
#include <iostream>
class Base {
public:
// virtual enables runtime polymorphism
virtual void show() { std::cout << "Base class\n"; }
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void show() override { std::cout << "Derived class\n"; }
};
int main() {
Base* b = new Derived();
b->show(); // calls Derived::show at runtime
delete b;
}
Git overview
# set at beginning
git config --global user.name = "Djordje Petrovic"
git config --global user.email = "dpetrovic@ethz.ch"
# init repo
git init
# add and create commit
git add <file>
git commit -m "commit msg"
# switch branch
git checkout -b <new_branch> # new branch
git checkout <some_branch> # existing branch
# merge branches
git checkout <branch-you-want-to-merge>
git merge <branch to merge>
git add . # fix merge conflicts (if any), then commit
git commit -m "merge: <branch-to-merge> into <current-branch>"
# undoing changes
git reset --soft HEAD~1 # one commit, commited changes to stage
git reset --hard HEAD~1 # one commit, completely delete
git restore --staged <file> # unstage (only > 2.23.0)
git reset HEAD <file> # reset changes since last commit
# move files where you want 'em
git stash # temporary store staged & unstaged changes (not untracked!)
<do something>
git stash pop # re-apply changes
# connect to remote
git remote add <server name> <server url>
git push --set-upstream <server name> <server branch name>
git push -u <server name> <server branch name> # short version
# clean up untracked files
git clean -fd
# view history
git log --oneline --graph --all
# fix last commit message
git commit --amend -m "new message"
libraries
Assuming the library is in tools.h and tools.cpp:
static
# 1. compile and archive into static library
g++ -c tools.cpp -o tools.o
ar rcs libtools.a tools.o # convention: add "lib" + ...
# 2. link static library when compiling program
g++ main.cpp -L. -ltools # -L. -> look in .; -l -> "lib" + "tools"
g++ main.cpp ./libtools.a # or link manually
shared
# 1. compile (with position-independent code)
g++ -c -fPIC tools.cpp -o tools.o
# 2. create shared library, add path (current folder) to enviroment
g++ -shared tools.o -o libtools.so
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=.:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
# 3. when compiling, link shared library
g++ main.cpp -L. -ltools
short command:
g++ -fPIC -shared tools.cpp -o libtools.so
make && cmake
makefile
$@- target name$<- first prerequisite name$^- name of all prerequisites
CXX=g++
CXXFLAGS=-Wall -Wpedantic -Werror
.PHONY all
all: main clean
# static library
tools.o: tools.cpp tools.h # include header to recompile when it changes
$(CXX) -c $< -o $@
libtools.a: tools.o
ar rcs $@ $^
main: main.cpp libtools.a
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $< -L. -ltools -o $@
# shared library
tools.o: tools.cpp
$(CXX) -c -fPIC $^ -o $@
libtools.so: tools.o
$(CXX) -shared $^ -o $@
main: main.cpp libtools.so
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $< -L. -ltools -o $@
@echo "run with: LD_LIBRARY_PATH=. ./main"
# clean
clean:
rm -f *.o *.so *.a main
cmake
- basic CmakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.2)
# project name
project(proj)
# require C++20 (optional)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 20)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
# sources (optional)
set(SOURCES tools.cpp main.cpp)
# static library
add_library(tools_static STATIC tools.cpp)
# shared library
add_library(tools_shared SHARED tools.cpp)
# executable linking to static library
add_executable(main_static main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main_static PRIVATE tools_static)
# executable linking to shared library
add_executable(main_shared main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main_shared PRIVATE tools_shared)
# install header, library, executable
install(FILES tools.h DESTINATION include)
install(TARGETS tools_static main_static
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin)
- to run:
# create build dir
mkdir build
cmake -S . -B build # create makefile
# build everything
cmake --build build
# run shared library version
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=build ./build/main_shared
advanced cmake installation:
CMAKE
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(MyFunc_Project LANGUAGES CXX)
# Build static library. If needed :STATIC -> SHARED
add_library(myfunc STATIC myfunc.cpp)
# Public include directory for the library
target_include_directories(myfunc PUBLIC
${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR})
# Build test program
add_executable(test_myfunc main.cpp)
# Link executable to library
target_link_libraries(test_myfunc
PRIVATE myfunc)
# ---------- Installation ----------
# Install header
install(FILES myfunc.hpp
DESTINATION include)
# Install library
install(TARGETS myfunc
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin)
# Install executable
install(TARGETS test_myfunc
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin)
containers
sequence containers (vector, deque, list, array)
- Construction / assignment
container()→ default constructorcontainer(n, value)→ fill constructorcontainer.begin() / container.end()→ iteratorscontainer.cbegin() / container.cend()→ const iterators
- Size / capacity
size(),empty(),capacity()(vector)resize(n),reserve(n)(vector)
- Element access
operator[],at()→ random access (vector, deque, array)front(),back()
- Modifiers
push_back(),pop_back()push_front(),pop_front()(deque, list)insert(pos, value),erase(pos)clear(),swap()emplace_back(),emplace()
associative containers (set, map, multiset, multimap)
- Element access
find(key)→ iterator to elementcount(key)→ number of elements with keyoperator[key]→ map only, inserts default if not exists
- Modifiers
insert(value)/emplace(value)erase(key)orerase(iterator)clear(),swap()
- Iterators
begin(),end(),cbegin(),cend()
unordered containers (unordered_set, unordered_map)
- Same as associative containers, but average O(1) lookup, insertion, deletion.
- Functions:
find,count,insert,erase,clear,bucket_count(),load_factor().
performance
- Vector: fast random access, slow front insertion/deletion
- Deque: fast front/back insertion/deletion, slower random access than vector
- List: fast insertion/deletion anywhere, no random access
- Set / Map: log(N) insertion/search
- Unordered_set / unordered_map: average O(1) insertion/search
performance
- Vector: fast random access O(1), slow front insertion/deletion O(N)
- Deque: front/back insertion/deletion O(1), slower random access than vector O(1)
- List: fast insertion/deletion anywhere O(1), no random access (O(N) traversal)
- Set / Map: insertion/search O(log N)
- Unordered_set / unordered_map: average insertion/search O(1), worst case O(N)
functions
empty(),size(),max_size()- Iterators:
begin(),end(),rbegin(),rend() swap(container1, container2)- Non-member:
std::begin(container),std::end(container)
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
// call lambda for each element (modify in-place)
std::for_each(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](auto &x){ x += 1; });
// transform each element, store result in same/different container
std::transform(vec.begin(), vec.end(), vec.begin(), [](auto x){ return x*2; });
std::transform(vec.begin(), vec.end(), out_vec.begin(), [](auto x){ return x*2; });
// compute sum / aggregate value
double sum = std::accumulate(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0.0, [](double acc, auto x){ return acc + x; });
// copy elements that satisfy condition
std::vector<int> filtered;
std::copy_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::back_inserter(filtered), [](auto x){ return x>5; });
// sort elements with custom comparator
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](auto a, auto b){ return a>b; });
// fill elements with a value
std::fill(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0);
// fill with sequential values
std::iota(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 1);
// reverse order
std::reverse(vec.begin(), vec.end());
// rotate elements so middle becomes first
std::rotate(vec.begin(), vec.begin() + 2, vec.end());
// remove elements based on value or condition
vec.eraseremove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0), vec.end();
vec.eraseremove_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](auto x){ return x<0; }), vec.end();
class functions
#include <iostream>
class MyClass {
int x;
public:
// constructors / destructor
MyClass() : x(0) {}
explicit MyClass(int v) : x(v) {}
~MyClass() = default;
// copy semantics
MyClass(const MyClass& other) : x(other.x) {}
MyClass& operator=(const MyClass& other) {
x = other.x;
return *this;
}
// move semantics
MyClass(MyClass&& other) noexcept : x(other.x) {
other.x = 0;
}
MyClass& operator=(MyClass&& other) noexcept {
x = other.x;
other.x = 0;
return *this;
}
// operators
MyClass operator+(const MyClass& rhs) const {
return MyClass(x + rhs.x);
}
MyClass& operator+=(const MyClass& rhs) {
x += rhs.x;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const MyClass& rhs) const {
return x == rhs.x;
}
int& operator[](int) { return x; }
// stream operators
friend std::ostream& operator<<ostream& os, const MyClass& m {
return os << m.x;
}
friend std::istream& operator>>istream& is, MyClass& m {
return is >> m.x;
}
};
istream and ostream:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
// file i/o
std::ofstream outfile("data.txt");
if (outfile.is_open()) {
outfile << "writing to file" << std::endl;
outfile.close();
}
// string streams (useful for parsing)
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "100 200";
int a, b;
ss >> a >> b;
// manipulators
#include <iomanip>
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << 3.14159; // prints 3.14
traits
#include <cmath>
// default trait: keep same type
template<typename T>
struct hyp_type { using type = T; };
// int -> return double
template<>
struct hyp_type<int> { using type = double; };
// alternative notation:
template<>
struct hyp_type<long> { typedef double type; };
template<typename T>
typename hyp_type<T>::type hypothenuse(T a, T b) {
using return_t = typename hyp_type<T>::type; // use the trait type
return static_cast<return_t>sqrt(a*a + b*b);
}
// static variables
template<class T> struct is_integral { static const bool value=false; };
template<> struct is_integral<int> { static const bool value=true; };
meta-programming
// compile-time loop unrolling via recursion
template<int I>
struct MetaDot {
static double f(const double* a, const double* b) {
// recursion: current index + result of previous indices
return a[I] * b[I] + MetaDot<I - 1>::f(a, b);
}
};
// specialization to stop recursion
template<>
struct MetaDot<0> {
static double f(const double* a, const double* b) {
return a[0] * b[0];
}
};
void compute() {
double v1[3] = {1.0, 2.0, 3.0};
double v2[3] = {4.0, 5.0, 6.0};
// compiler expands this to: v1[2]*v2[2] + v1[1]*v2[1] + v1[0]*v2[0]
double result = MetaDot<2>::f(v1, v2);
}
exceptions
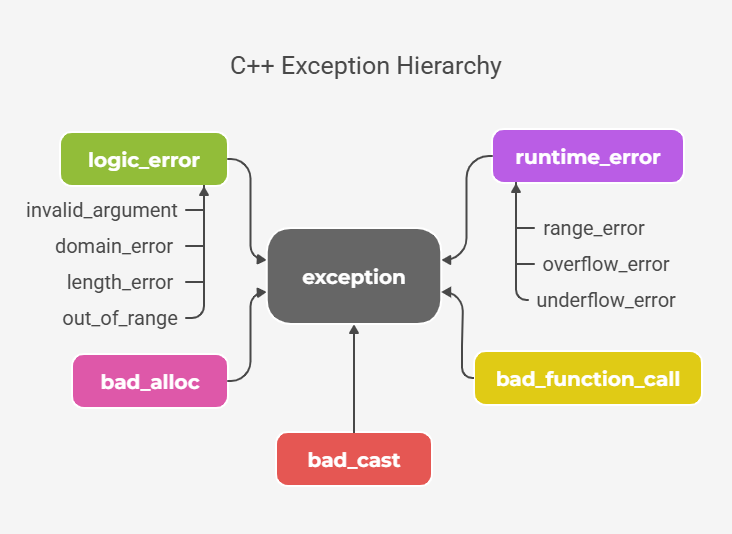
try{
// some code which throws
} catchinvalid_argument& e){ // or std::exception (more general
std::cout << "invalid argument catched\n";
} catch (...){
std::cout << "default case catched\n";
}
// throwing an exception
#include <stdexcept>
void check(int x) {
if (x < 0) throw std::invalid_argument("negative value");
}
chrono
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>
std::vector<std::chrono::duration<double>> times = {};
auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// some operation
auto finish = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
times.push_back(finish - start);
//OR
auto t_start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i< N; ++i) double result = std::sin(1);
auto t_end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = static_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(t_end-t_start).count();
notes
- unit stride
sequential memory access (best in inner loop) - Loop Unrolling: Reducing loop overhead by processing multiple elements per iteration.
- Inlining: Using
inlineor defining functions in headers to suggest the compiler replace the call with the actual code. - Static vs Dynamic Linking:
- Static: Binary is larger but self-contained. No runtime dependency.
- Dynamic: Binary is smaller. Multiple programs can share one .so/.dll in memory.